


Next: Introduction
Up: Path Integral Monte Carlo
Previous: Contents
Contents
- BRW
- Brownian random walk,
- DE
- Direct estimator,
- EOS
- Equation of state,
- FP
- Free particle,
- MC
- Monte Carlo,
- PIMC
- Path integral Monte Carlo,
- PPT
- Plasma phase transition,
- RPA
- Random Phase Approximation,
- TE
- Thermodynamic estimator,
- VDM
- Variational density matrix,
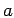
- Wigner-Seitz radius,
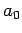
- Electron Bohr radius,
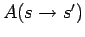
- Acceptance probability for MC step
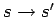 ,
,
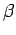
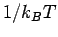 ,
,
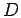
- Spatial dimension, here 3,
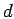
- Amplitude parameter in Gaussian density matrix,
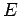
- Internal energy per atom,
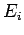
- Internal energy of state
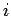 ,
,
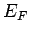
- Fermi energy,
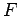
- Free energy,
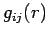
- Pair distribution function of species
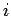 and
and 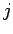 ,
,
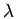
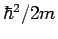 ,
,
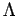
- Thermal de Broglie wave length
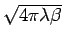 ,
,
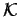
- Kinetic energy operator,
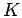
- Kinetic energy function,
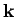
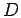 dimensional reciprocal lattice vector,
dimensional reciprocal lattice vector,
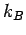
- Boltzmann factor,
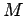
- Number of time slices,
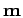
- Position vector in Gaussian density matrix,
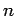
- Number of particles per unit volume, for hydrogen atoms per unit volume,
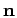
- Integer vector in
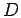 dimensions,
dimensions,
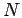
- Number of particles,
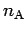
- Order in expansion formula 2.38 used to calculate the pair action,
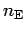
- Order in corresponding expansion formula 2.38 for the energy,
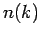
- Momentum distribution,
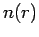
- One particle reduced density matrix,
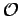
- Operator in quantum mechanics,
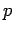
- Pressure,
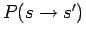
- Probability for MC step
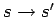 ,
,
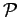
- Permutation of identical particles,
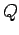
- Electronic charge of one ion,
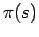
- Probability of state
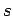 ,
,
-
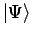
- Hilbert vector,
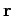
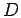 dimensional coordinate vector,
dimensional coordinate vector,
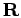
- Set of coordinates of
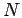 particles in
particles in 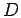 dimensions,
dimensions,
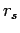
- density parameter
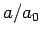 ,
,
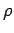
- Density matrix,
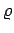
- Mass density
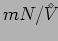 ,
,
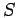
- Action in path integral,
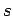
- State in configuration space,
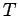
- Temperature,
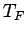
- Fermi temperature
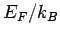 ,
,
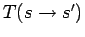
- Sampling distribution for MC step
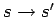 ,
,
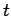
- Imaginary time,
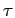
- Time step in path integrals,
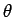
- Degeneracy parameter
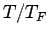 ,
,
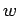
- Width parameter in Gaussian density matrix,
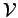
- Potential energy operator,
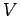
- Potential energy,
-
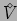
- Volume of the simulation cell
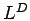 ,
,
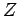
- Canonical partition function.



Next: Introduction
Up: Path Integral Monte Carlo
Previous: Contents
Contents
Burkhard Militzer
2003-01-15